INFANCIA Y EDUCACIÓN EN LA ANTIGUA ROMA GABRIEL ROSSELLÓ, ESCRITOR
The fragments were obviously re-used at a later stage as paving slabs: they may be arranged to form four unconnected portions (Fragments A-D) of a senatorial cursus of Imperial date relating to one M. Hirrius Fronto Neratius Pansa, known to us hitherto only from fragmentary and uncertain references. Previously, in fact, we only knew of him as.

El cursus honorum, la carrera política de la antigua Roma hasta el Senado
Updated on February 28, 2018 The order of advancement through elected offices (magistracies) in Republican Rome was known as the cursus honorum. The sequence of offices in the cursus honorum meant that an office couldn't be skipped, in theory. There were exceptions. There were also optional offices that could be steps along the cursus honorum .

¿Qué era el cursus honorum en la antigua Roma?
GETO-DACIAN RELIGION GETO-DACIAN RELIGION . The Getae and the Dacians were ancient Thracian peoples who lived in Moesia, on the northern plain of the river Danube, and in the Carpathian Mountains, approximately in the territory of modern-day Romania and Moldova. Although the religion of the Getae and the Dacians escapes complete reconstruction, it forms, nevertheless, like the religion of the.
.jpg)
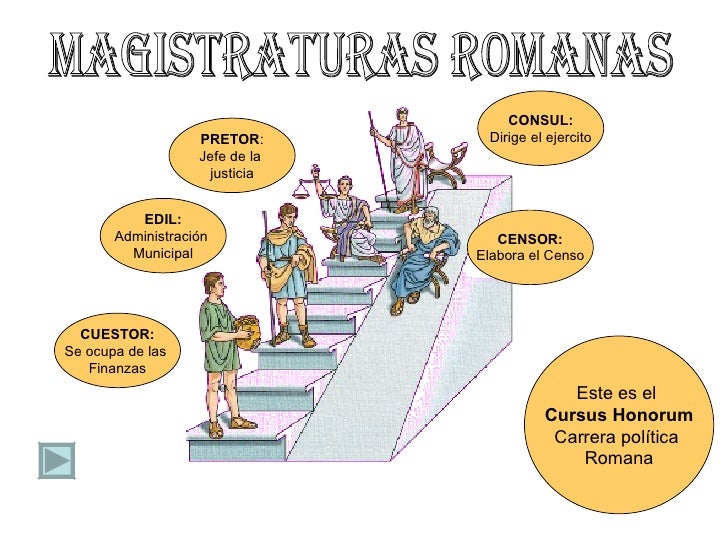
APASIONADOS DEL IMPERIO ROMANO CURSUS HONORUM ROMANO
Cursus honorum ("career path," earliest testimonies in Cicero) refers to the order in which Roman politicians were expected to rise through the ranks of public offices ( honores ). More generally, the term became synonymous with the hierarchy of magistracies at Rome.
APASIONADOS DEL IMPERIO ROMANO ¿QUÉ ERA EL CURSUS HONORUM?
Res nullius is a doctrine. The expression "res nullius" (lit: nobody's thing) is a Latin term derived from private Roman law whereby res (an object in the legal sense, anything that can be owned, even a slave, but not a subject in law such as a citizen, nor land) is not yet the object of rights of any specific subject. Such items are considered ownerless property and are free to be acquired by.
Thème 5 leçon 2. l'Empire romain (leçon complète) Une autre histoire
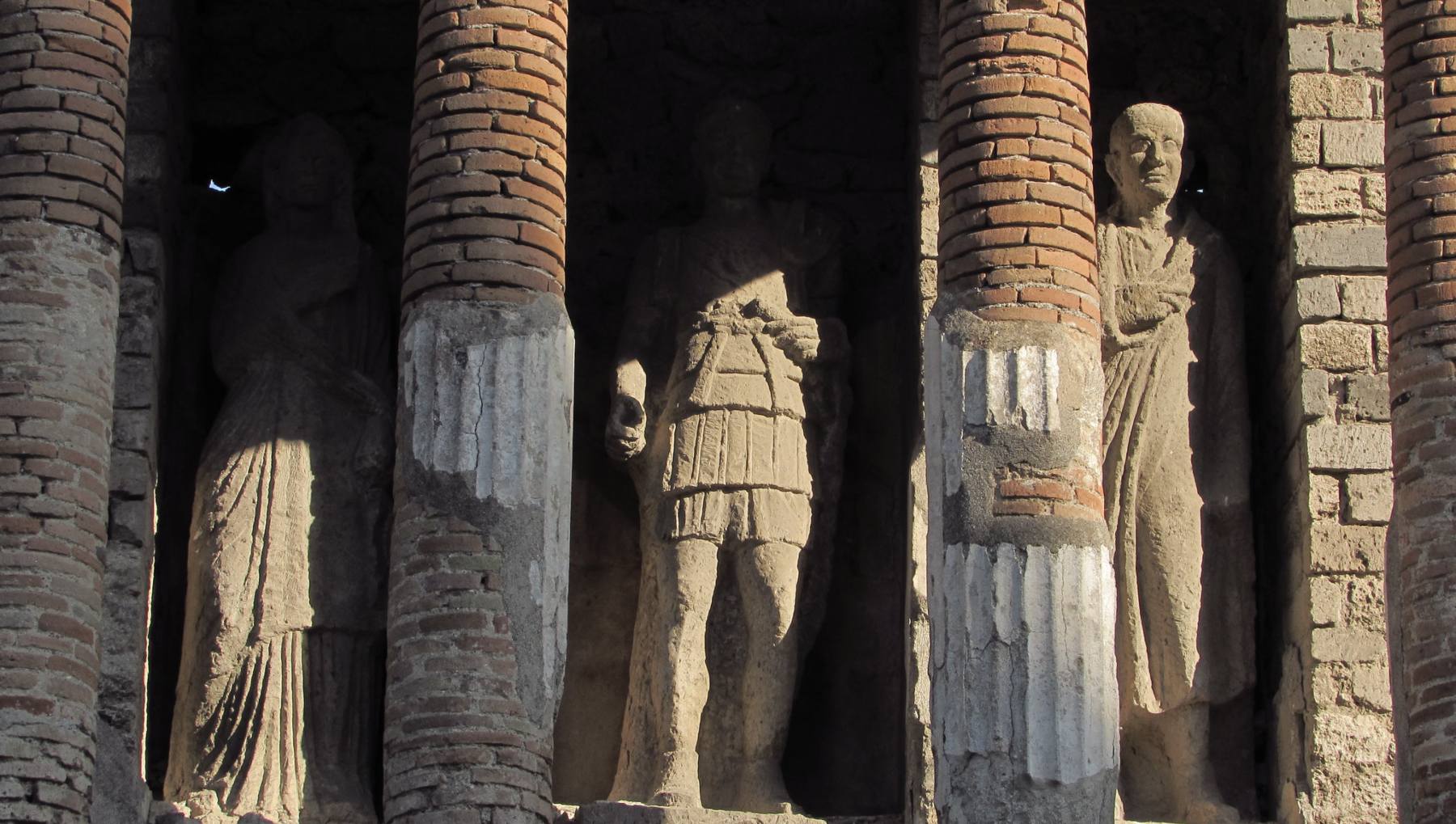
Part of the project La Roma della Repubblica.Il racconto dell'Archeologia, the exhibition is dedicated at the public charges of the members of the republican age, the cursus honorum, a basic part of the political life in the ancient Rome.. The main characters in this tale are five anonymous figures portrayed by the five statues that provide an exceptional storytelling experience: four of them.

Cursus Honorum I Die Ämterlaufbahn der Römischen Republik YouTube
cursus honorum Roman government Learn about this topic in these articles: history of Roman consulship In ancient Rome: Citizenship and politics in the middle republic.moved swiftly through the senatorial cursus honorum ("course of honors") to win the consulship and command against Philip V at the age of 30.

“Cursus honorum. The government of Rome before Caesar”, the exhibition at the Capitoline Museums
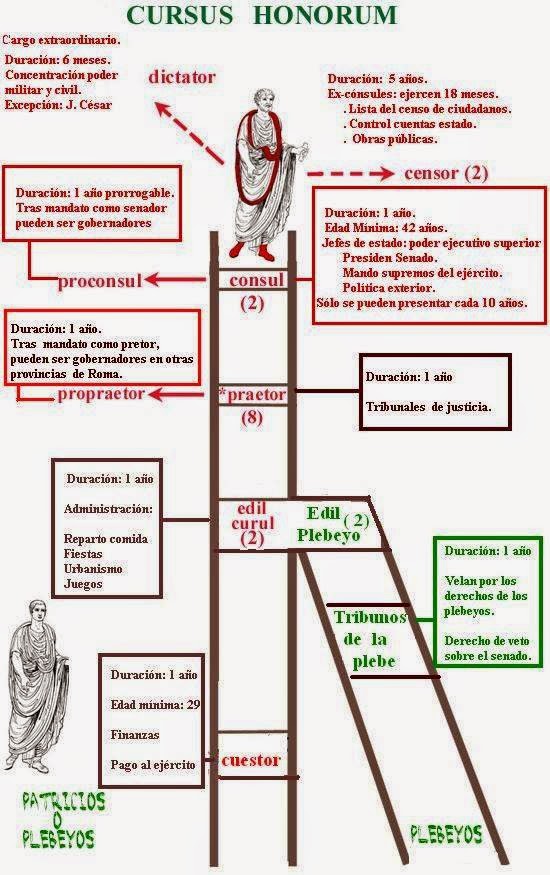
Abstract. This chapter reviews Plutarch's unusual familiarity with the Roman senatorial career pattern, the cursus honorum. A Roman statesman was honoured according to the offices he had held, the victories he had won, and the triumphs he had celebrated. Offices were held in sequence, and formed a cursus, a standard career path: quaestor.

Cursus Honorum. Il governo di Roma prima di Cesare
Reconstructing Honor in Roman Philippi Carmen Christi as Cursus Pudorum , pp. 34 - 63 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511487972.003 Publisher: Cambridge University Press Print publication year: 2005 Access options Get access to the full version of this content by using one of the access options below.

cursus honorum Histoire de rome, Histoire médiévale, Cours histoire
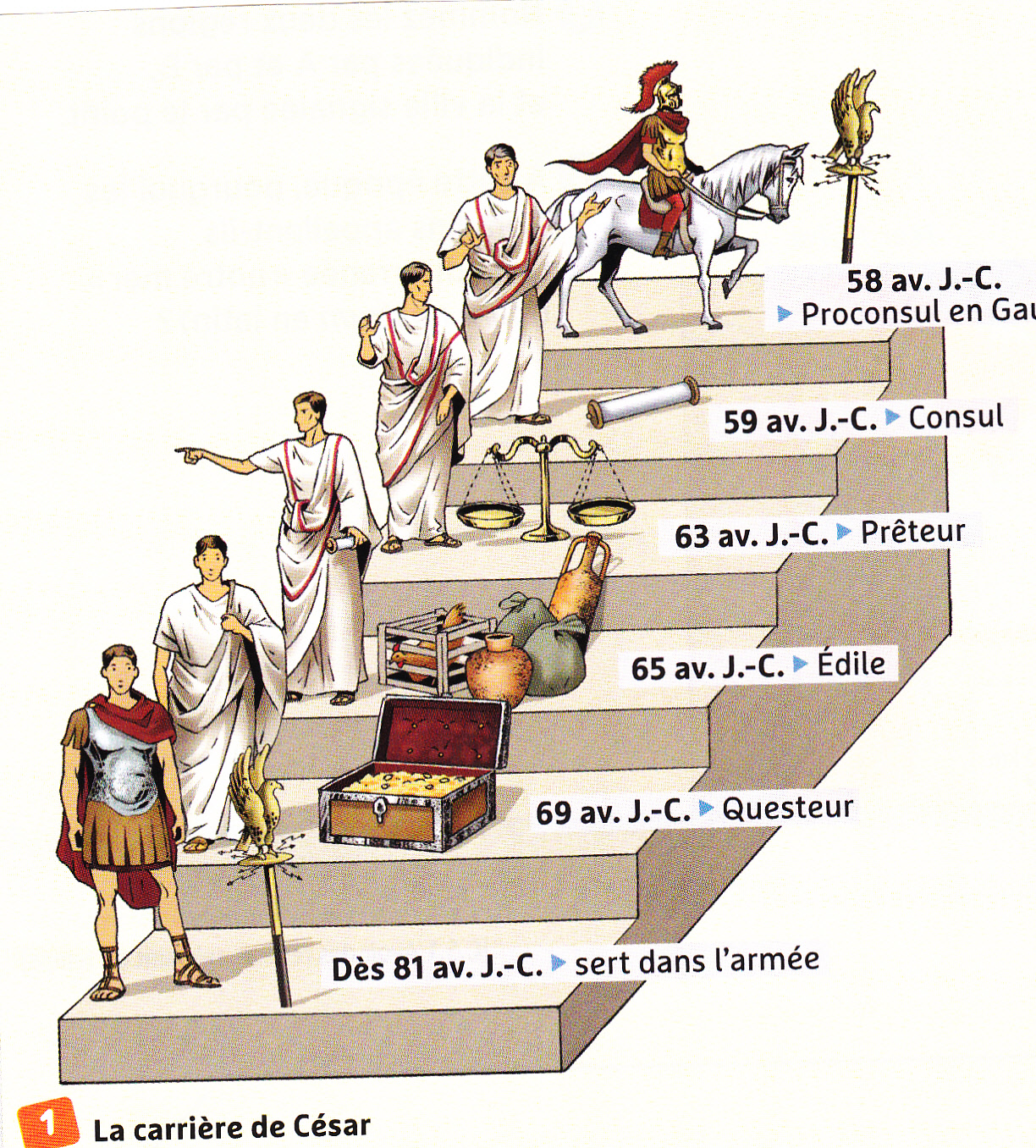
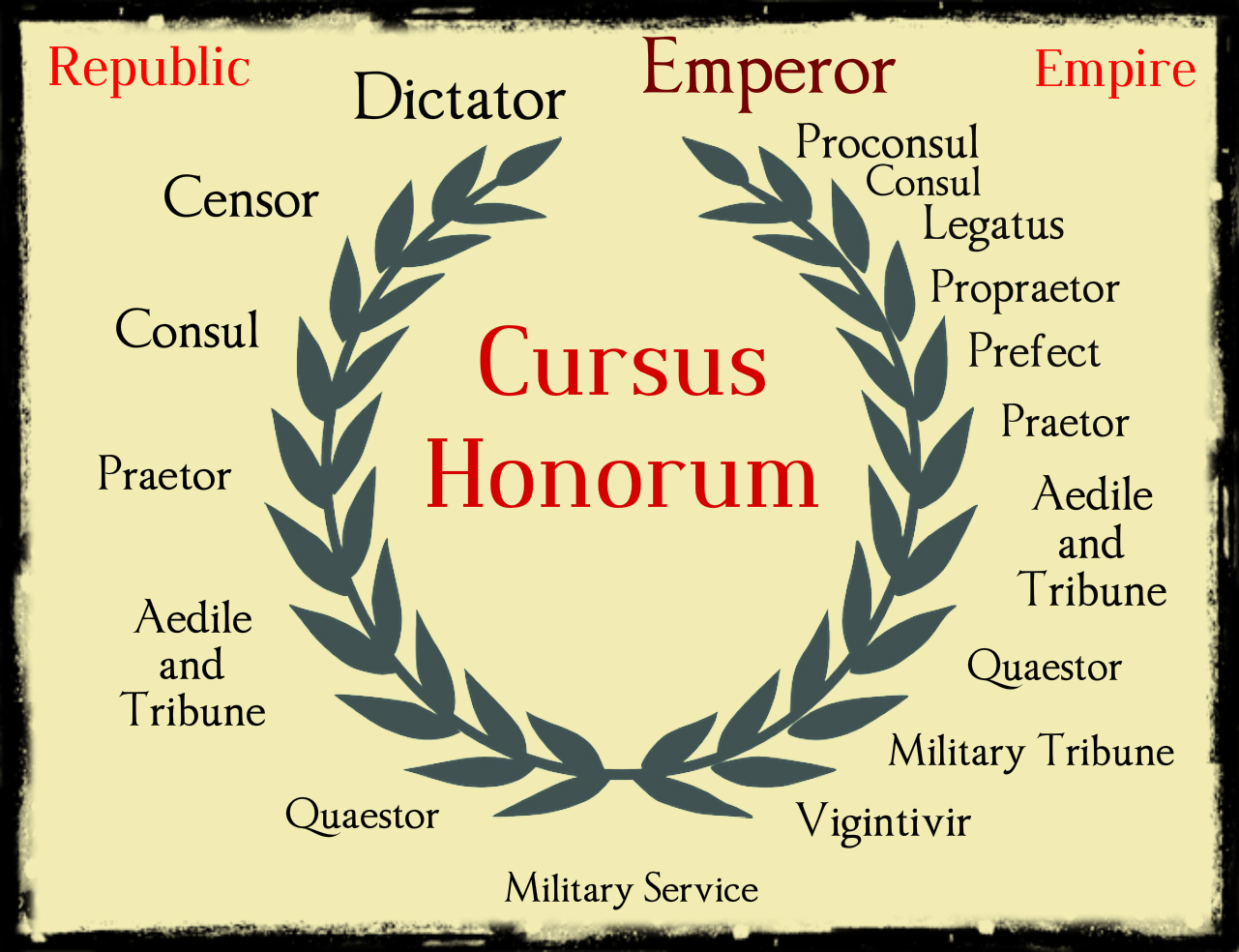
The cursus honorum ( Latin :'course of honors') describes the ancient Roman system of political advancement. It was a sequence of offices, often thought of as a metaphorical ladder, that an individual could hold, with each office requiring greater experience, and affording a higher level of prestige.

cursus honorum esquema Búsqueda de Google Roma antigua, Historia romana, Roma
in A Dictionary of World History (2) Length: 149 words View all related items in Oxford Reference » Search for: 'cursus honorum' in Oxford Reference » The name given to the ladder of (annual) offices that would-be Roman politicians had to climb.

El cursus honorum, la carrera política de la antigua Roma hasta el Senado
Cursus honorum Roma Antiga Este artigo é parte da série: Política e governo da Roma Antiga Períodos Reino de Roma 753 a.C. - 509 a.C. República Romana 509 a.C. - 27 a.C. Império Romano 27 a.C. - 395 Império Ocidental 395 - 476 Império Oriental 395 - 1453 Principado Dominato Constituição romana Constituição do Reino Constituição da República
the cursus honorum in ancient Rome
In The Cursus Honorum: A Study of the Origins and Evolution of Sequential Ordination, John St. H. Gibaut examines the development of the sequential ordination through the grades of the Church's ministry. Although the cursus honorum has long been an assumed part of the ordination process, Gibaut demonstrates that it had a varied and complex history.

Roman Government
Cursus honourum, literally "path of honour", was a well-established ladder of political career in the Roman Republic. In Rome, it gradually became a custom that soldiers held successive offices. It was the beginning of the concept of a "political career". In practice, the political career involved men from senatorial families.

CURSUS HONORUM
Rome's political arena was a fiercely competitive one. In this video, we will take a closer look at Rome's ladder of political offices, the so-called Cursus.
APASIONADOS DEL IMPERIO ROMANO ¿QUÉ ERA EL CURSUS HONORUM?
El Cursus Honorum (curso de honor) era el nombre con el que se conocía tanto en la República Romana como en el Imperio Romano al orden secuencial de cargos públicos, tanto políticos como militares, que un hombre romano de buena familia debía ir asumiendo y completando a lo largo de su vida para así subir en la escala social romana.